Wu X, Zhang X. Automated inference on criminality using face images[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.04135, 2016: 4038-4052.
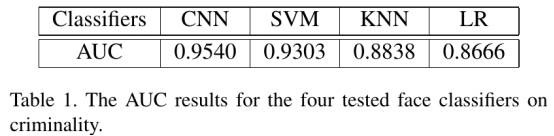
该篇论文利用supervised machine learning(logistic regression, KNN, SVM, CNN) 对criminal (C) 和non-criminal (N) 面部图像进行分类(准确度最高达到89.51%),并进行一些实验分析C与N群体之间的区别:
- N群体内部的面部相似度更大,C群体内部的面部差异更大。
- C和N是两个concentric(同心), distinctive的manifold(流形).
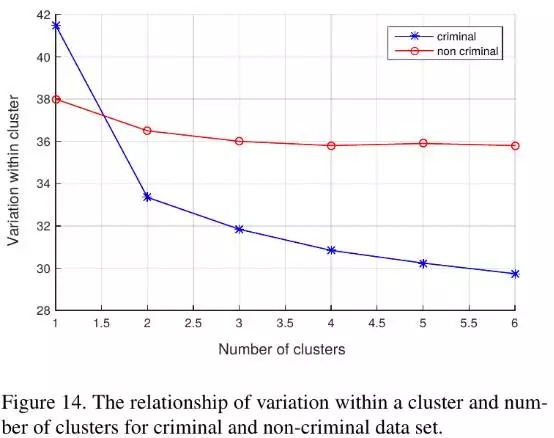
- The variation of C greater than N.
基于面部特征的人为判断会带有偏见、先决条件等,而CV算法并不会存在这些问题。
1. Data Preparation
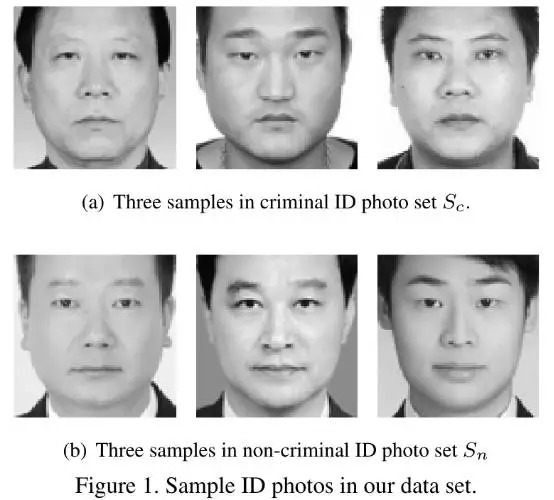
- Dataset包含1856张照片 (1126N+730C, Figure 1). 照片标准: Chinese, male, between ages of 18 and 55, no facial hair, no facial scars, or other markings.
- N including waiters, construction workers, taxi and truck drivers, real estate agents, doctors, lawyers and professors; half have university degrees.
- C including the ministry of public security of China, the departments of public security for the provinces of Guangdong, Jiangsu, Liaoning, etc. And the City police department in China.
- C中 235人是violent crimes (murder, rape, assault, kidnap and robbery), 剩余536人是non-violent crimes (murder, rape, assault, kidnap and robbery).
- Only the region of the face and upper neck is extracted.
- 80 × 80 images.
- 将每张图像的直方图与整个数据集的平均直方图相匹配,从而使得灰度图归一化到同样的强度分布。

2. Methods
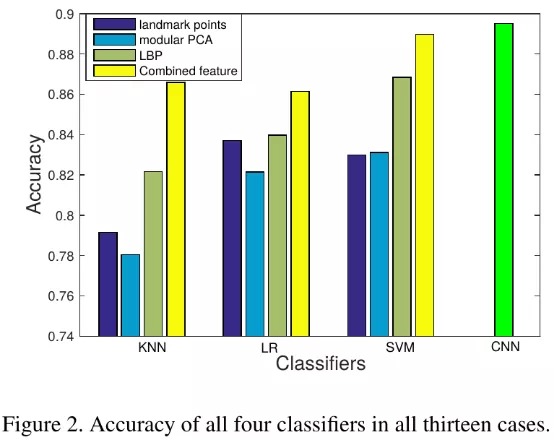
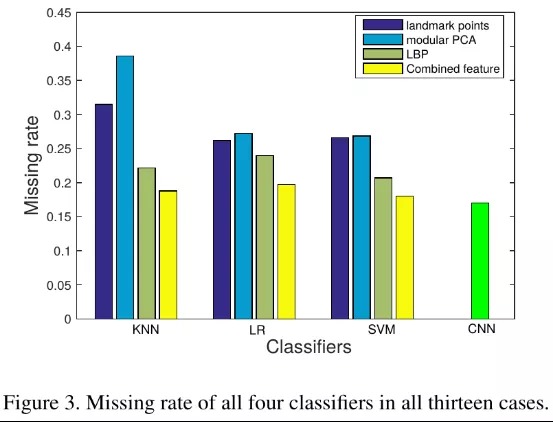
- 面部关键点特征能够避免signal level和variant of source cameras的影响。论文使用以下四种关键点:
- Facial landmark point.
- Facial feature vector, generated by modular PCA.
- Facial feature vector based on Local Binary Pattern (LBP) histograms.
- The concatenation of above three feature vectors.
(Feature-driven classifiers (LR, SVM, KNN) 3 + Data-driven classifiers (CNN)) 10-fold cross validation = 130 cases
3. Results
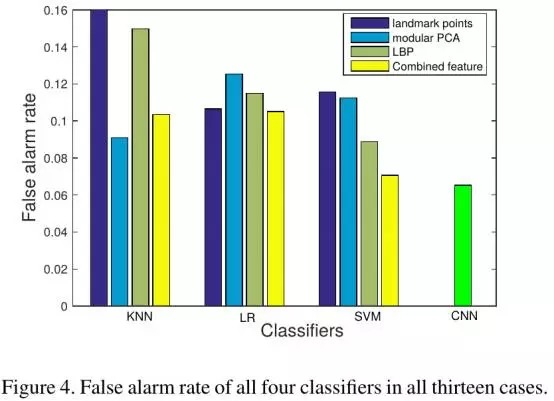

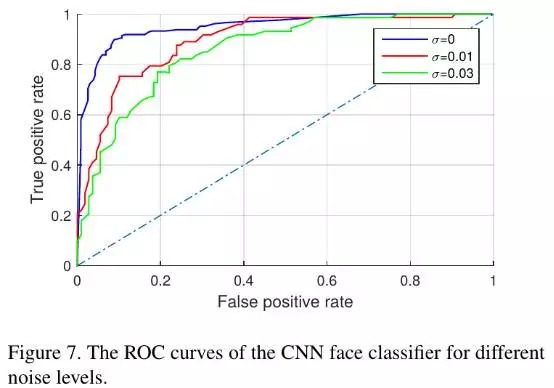
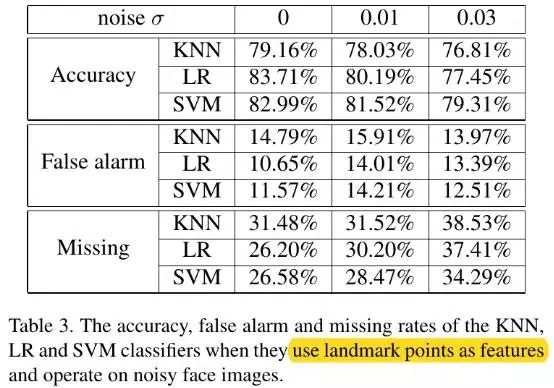
- 不同的source camera拍摄的照片可能会带有不同camera的signatures, 虽然已通过上述的landmark point解决,但在此进一步引入高斯噪声 (mean=0) 来overpower camera signatures. 实验结果与期望的一致: 性能不会出现很大的变化 (Figure 6,7;Table 2, 3).


4. Discriminating Feature
- 使用Feature Generating Machine (FGM)进行分析与犯罪最相关的面部部位,得出这些特征位于眼角、嘴唇和额头部位 (Figure 8).
- ρ: 上嘴唇的曲度
- d: 内眼角之间的距离
- θ: 鼻尖到嘴唇两角的角度
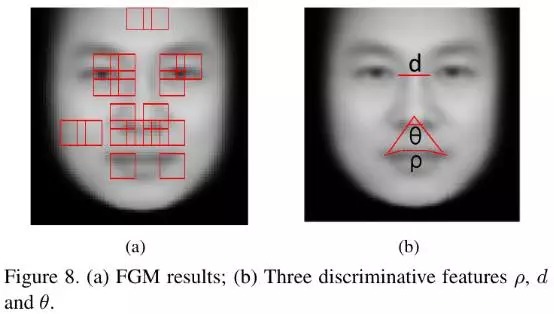

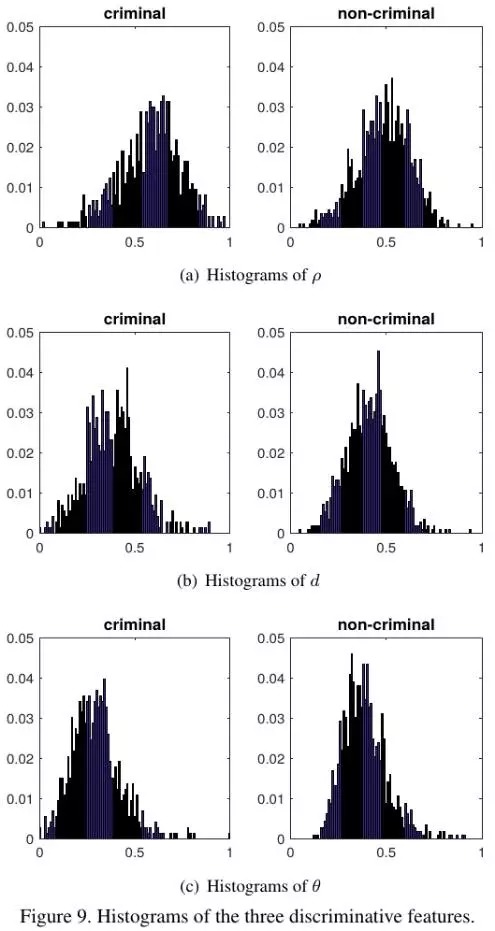
- 使用Hellinger距离分别计算C和N两者之间的上述3个部位的距离,分别为0.3208, 0.2971, 0.3855. 因此,C和N是存在一定差异的.
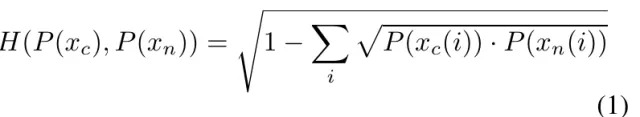
- 按照论文分析结果 (Figure 8, Table 4)脑补了一个极端的罪犯例子
- 三个特征的直方图
5. Face Clustering on Manifold
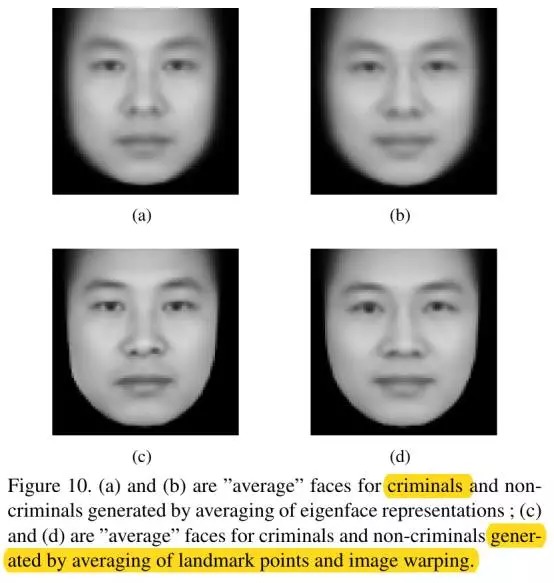
- 通过平均脸并不能很好地得出C和N群体的区别 (Figure 10),因此需要在更高维度 (manifold流形和聚类)上进行分析。

- 公式2分别为cross-class average manifold和in-class average manifold.

- 计算得到manifold后,使用Isomap进行降维可视化。